UPDATING THE PENNY METHOD
A while back I posted about using a penny, a cell phone, and a bit of math to determine the thread count of linens, both evenweave and skew. And now the US penny is quickly charging to extinction, abandoned by the US Mint, and soon to disappear entirely from circulation. Which means that I need to issue an update.
Voila!
The Dime Method.

I picked the dime because it’s smaller than the nickel or quarter, and easier to count around the outside edge without losing your place. Counting the threads totally covered by the dime, heading north to south, we get a total of 26. And by counting the number of totally covered threads east to west, we also get 26. The first conclusion is a happy one. We have an evenweave.
Now for the math.
The official diameter of a US dime, as stated by the US mint, is 0.705 inch (17.91mm). I will continue the math here with threads per inch rather than metric to avoid confusing US folk, but the same method works perfectly well with metric measurements. And if you know the measurements of any other coin used anywhere else in the world, you can adapt this for local convenience, worldwide.
So what we have is 26 threads over 0.705 inches. We divide 26 by 0.705 and we get 36.88 (roughly). We can round that up to 37. My fabric in this sample is 37×37 threads per inch.
Let’s confirm that.

Yes, 37.
And you are right that’s a decimal inch ruler. I am proud to be an Engineer’s Daughter, and have many of my dad’s old drafting aides. I deliberately did NOT add any assisting lines to the ruler photo as proof of my assertion that it is FAR easier to count the threads obscured by the coin, going around the edge of the coin, than it is to do a straight line count across a ruler’s edge. It’s also FAR more likely that I would have a dime handy than a ruler in my pocket when I am out and about in the wild.
Try again. This time finer.

I get 31 in the north-south direction and 28 in the east west direction. This piece of linen is a skew count, with more threads in the vertical than the horizontal. Doing the math:
- Vertical (north-south) 31/0.705 = 43.97, rounded up to 44 per inch
- Horizontal (east-west) 28/0.705 = 39.71, rounded up to 40 threads per inch
Now, does a skew count mean that effective countwork can’t be done? Absolutely not. Here is the piece that I used for the second example:

The slightly skew count means that over the same length there are more stitches in the vertical direction than there are in the horizontal. My mermaids are then a bit squished in height compared to their width because the vertical stitches are a tiny bit shorter than the same number of stitches over the horizontal. But the only place that this is evident are the large, symmetrical flowers just above their tails. You can just make out the height elongation in them because (logically) they are supposed to fill a square volume, not a rectangular one. Here is an old post that discusses this challenge further, and shows what happens when you wrap a design around a corner on a skew count fabric, and confesses that flipping your measurements is an easy mistake that even I make..
For the record, I stitched this piece in 1994, from a chart I redacted myself. The photo source that I worked from was in Schuette and Mueller-Christensen’s Pictorial History of Embroidery. I presented this chart along with my own original accompanying border on Plate 75 in my own The New Carolingian Modelbook, published in 1995.
As for the piece I used for the first example? The full Don’t Panic chart is a free download on my embroidery patterns tab, right here on String-or-Nothing.
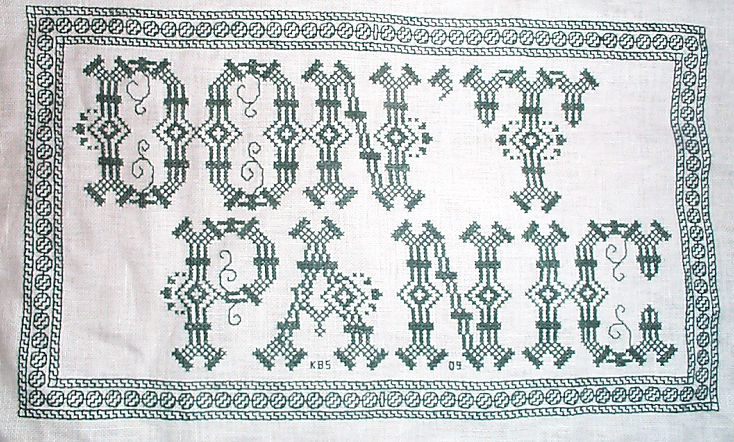

Don’t Panic is in fact the best advice I can give to the math anxious among us.
TWO COLOR DOUBLE RUNNING STITCH – TWICE THE FUN
As promised, here is a round-up of what I’ve been looking into on double running stitch, done in two alternating colors. First, heartfelt thanks to Melinda Sherbring and the gang over at the Facebook group Historic Hand Embroidery.
I knew I had seen examples of this type of work on samplers, but my own research notes are particularly poor in samplers. I tend to focus on the small fragments of household and body linen that lie quietly and largely unnoticed in museum research collections. Samplers receive far more attention, are often under licensing restrictions or have been fully charted by reproduction houses. So in a fit of laziness (it being vacation) I put out a call to the group and asked for assistance. Many people responded, Melinda especially so, furnishing 85% of the material I will cite below. So copious thanks, Melinda! I bow to your greater expertise on these, and will accept any/all corrections.
First, here’s what I am talking about. Here is a simple graph of a sprig pattern, worked in double running of a single baseline.

Note the alternating color stitches in the baseline. If I were to stitch this, I’d start with black, take that first stitch at the baseline’s left edge, then in double running work the rest of the first flower in black as a detour from my baseline. When I returned to the baseline, I’d continue on to the next black stitch, then I could continue working the whole thread of black until I ran out, carefully counting the units between black flowers. After that I’d start again from the left, filling in the missing green stitch, and taking detours to work the green flowers. Or I could do it the easier way – parking my black threaded needle, taking up a green one, and working green stitches until I got to the first green flower, working that as a detour in the standard manner, and marching on for a few stitches after, then catching up and leapfrogging ahead with the black. Note that using two colors means one will always be traveling along the baseline in the same direction. There is no doubling back to fill in second pass double-running stitches as one can if a single color is used.
After some experimentation, I found the “leapfrog” method far easier, in spite of having to be careful not to snag the parked thread. Less long distance counting means fewer errors for me. I suspect that close examination of encroachment on these historical pieces will turn up that leapfrogging was the way they did it, too. It’s just so intuitive and so much simpler.
One more observation – an alternating baseline is a giveaway that the band was done in double running. It would be quite awkward and wasteful of thread to achieve this effect in back stitch. And using back stitch to do the branching detour sprigs would mean having to terminate the thread on each one, or stranding over to return to the baseline. Again, something wasteful to be avoided.
Examples
Melinda provided far more than these photos, but I am cherry picking the ones with details that display the best. Click on the sampler institution/accession/date link to see the full pieces. A couple more of Melinda’s citations are at the end of this post, for those who want to do their own deep dive.
Ashmolean WA2014.71.3 (1631-1700) The boxers/urns panel has a companion border at the bottom with alternating pink/blue sprigs and a clear two-tone baseline. There’s also another pair of companion borders at the bottom that uses a band of green stitching with the alternating color sprigs and two-tone baseline immediately along its edge:

Ashmolean WA2014.71.27 (mid 1600s) has the alternating color sprigs on a two-color baseline on the topmost motif. This is the one I dimly remembered from tiny illustrations in a sampler book. Note that additional satin stitching was done in the centers of the motifs to bring extra dimensionality and color, but the double running outlines are still there.

Burrell 31.7 (1640-1670) Sadly, no high resolution image. But on the bottom-most strip – its framing border, top and bottom strongly looks like two-tone sprigs, and probably has an alternating baseline but it’s hard to make out the detail on the baseline. More investigation on my part needed. As an aside, it’s nice that the Burrell gives thread counts for the linen ground – 28 warp x 25 weft per cm, or 71.12 x 63.5 threads per inch. I’ve included the main strip because it or a close sibling pops up in connection with alternate two-tone borders in other works.

Burrell 31.9 (1640-1670) Third strip from the bottom. Again, certain ID limited by photo quality, but it does look like that much wider strip was done with a two-tone WIDER baseline (same spirit as mine, but a different pattern), with alternating color detours. Shares a lot of the aesthetic and some bands with Burrell 31.7 – interesting!

Cooper Hewitt 1981-28-70 (1600s) Love their high resolution photos. Another clear hit. The companion border around the bottommost wide strip, for sure – done in at least THREE colors (wow!) with a multicolor baseline and single color sprigs. A green, a blue, and possibly a red and a pink, the red and pink are very much faded. Or it might just be green, blue, and pink. It’s very hard to parse but it does look like the baseline was done in pink-green-red-blue-pink-green-red-blue, which would leave very long skips, overlapping on the reverse. I’d love to see the back to confirm that, and to confirm the number of colors.

There are more possibilities on this same piece, but for the most part they are heavily overstitched in satin stitch or (possibly) hollie point or another detached looping/weaving stitch, worked on the outline and for the most part obscuring it. It also looks like the second color was not necessarily used on the double running stitch outline for the sprigs, but was employed in the fill treatment Here’s one with an alternating baseline of blue and pink(?). The pink looks like it was used to outline the acorn and leaf shapes with double running. Pink and green were used for the detatched stitch fills for the acorn and leaf, but the blue of the baseline seems to have ben employed to fill the twigs between the acorns and leaves.

Fitzwilliam T.59-1928 (circa 1680) I stumbled across this one looking for the other items Melinda cited. I saw tiny black and white photo of this in one of the first embroidery history books I borrowed from the library – a book published before 1965 or so. I charted some of the strips from it with a magnifying glass, and used them on a piece I did in high school, long before I found the SCA. I haven’t seen this piece since. (People looking to chart now have no idea how much easier it is today with on line access to zillions of primary sources and high resolution photos, all of which can be enlarged right on the screen. A far cry from being smuggled into university libraries to stare at fuzzy microfiche images, or taking magnifying glasses to low quality black and white photos in books.) There is clearly a two-tone companion border with an alternating color baseline accompanying the prominent rose band:

By way of contrast, this bit from the same sampler was NOT done with a two-tone baseline. Even if there are pink straight stitches between the green diamonds and other motifs in the uniting center band, those sprouting leaves in pink are independent from the true baseline, which is solid, unbroken green.

Fitzwilliam T.61-1928 (1677) Also stumbled upon, and sadly a bit blurry. Two possibilities in the photo below – and the lower wide border to which one of the candidates is the companion one looks to a design that’s a cousin to the one from the Burrell sampler above. The two-tone companion is clearly not the same design, even though it’s difficult to see.

More citations:
Ashmolean WA2014.71.44 (1633) Not a sharp photo, but the red/green framing bands on the boxers strip does look like it is probably done in the dual tone baseline, alternating color detour method.
Fitzwilliam T.82-1928 (1691). Looks like there could be a couple of candidate bands, especially in the framing borders around larger strips, but the photo resolution isn’t quite there, and I can’t be sure that the colors are united by a two-tone baseline. I need to do more investigation.
Conclusions:
I have not seen this treatment in portraits, or in fragments of household linen – only on band samplers. I will keep looking, but I think Melinda’s generosity makes it clear that double running done in two colors, with a two-tone baseline and sprigs alternating between those colors was a 17th century innovation, popular in England of that era. She has given us lovely data points from 1629 to the 1690s. Given the paucity of extant samplers before 1600, that is to be expected. Thanks again Melinda!
But I never say never. All I can say is “I haven’t seen it yet.” And who knows, maybe someone out there HAS a citation for use of this technique before 1625, a sighting in works from other times/locations; or evidence on a textile fragment or portrait that it was used on clothing or household linen. If so, please add a comment with that reference here, and I’ll be happy to do a follow-up post.
And my own progress?
I’m up to the outer framing border. I just realized that I forgot to plot the way the wreath-springs work in the corners, so I will do that later or tomorrow, and concentrate on finishing out the upper edge tonight.

Yes, the colors are a bit disjointed, and I’m not entirely pleased with how prominent the diagonals turned out. But I am working under severe materials quantity constraints. Most of the colors were too light to show well in this style of work, and those that are are in single 8 yard six-strand skeins, most of which were already nibbled by the original owner for her prior projects. I am still splitting each strand of the six, to double the yardage, but it’s going to be tight.
MORE GOODIES FOR THE CHATELAINE
The second half of my 2025 Toy Allowance has arrived! I bought more pieces for the stitcher’s chatelaine Younger Spawn gave me for the holiday in 2023.

Here’s a roundup of all of the components.
First, rose pin and majority of chains. Not sure where the Offspring picked that up. I noted several vendors selling near identical unpopulated chatelaines last year, but this year the rose design isn’t popping up.
First on left – the laying tool. This is a standard steel laying tool, not a fancy one made for display wearing. The Resident Male gave it to me about 5 years ago, along with the super-precise sharp scissors that are also on this chain.
Next, up by the rose is a needle threader. It’s a fine wire style threader encased in fancy findings. This is a new purchase from Beaddoodads, an Etsy shop based in Australia. It’s lovely and works quite well. A much welcome addition. I have a note in to the seller to find out if the threader can be replaced when it eventually and inevitably breaks (those skinny wire ones are only good for a year or so). In the mean time I’m literally keeping it on a short leash and will look to see if there is some sort of protective sheath I can devise for the working end.
On the long dangle next to the threader is my spool cage. This is also new, and as you can see, is home-made. I twisted it from the protective cage or bail that holds champagne corks in place before the bottle is opened. I may go back and do another. This one is from our New Years Eve bottle. Our anniversary bottle was silver tone instead of brass color. It’s just big enough to hold a full spool of the Corticelli silk I’m using now, and snug enough to keep it from unsupervised unreeling.
Back up we find a needle case, also new, and also from Beaddoodads. It has three small rubber or silicon gaskets that keep the slip on top securely in place, even while hanging.
Next over the the little purse accessory that Offspring included with the original gift. I softened some beeswax generously shared with me by a hyper-local beekeeper (Hi, Kevin, who lives around the corner!), and then molded it into one side of the snap enclosure holder.
Up again towards the rose is the last of the three new bits from Beaddoodads – the bobbin reel. It’s the long pin-like object holding the bobbin of plum color thread. In theory it is long enough to hold three metal bobbins. I only had one empty one to hand. I’ll probably replace it with three inexpensive generic metal bobbins. This one is for my ancient Elna SU sewing machine. Klaatu is very finicky about bobbins, and Elna ones of the correct vintage are hard to come by. It’s also worth noting that the bobbin reel is long enough to use with one of the little wooden Corticelli spools. Once one of those is empty, I’ll probably be using it instead of metal bobbins.
And last on the right is the pair of embroidery scissors that I got from the Resident Male along with my laying tool. Notice how it is chained. If I attach the lanyard clasp to just one of the scissor’s finger holes, gravity and movement eventually open the scissors. Those blades are stabby, plus I don’t want to damage them. By threading the chain through both loops, the scissors stay closed after use. And doing so is no impediment to ease of use.
Finally we have the ribbon to which this weighty seven-armed octopus is pinned. Together with all of its parts, my chatelaine is quite heavy. The needle case is surprisingly weighty, and the little purse is no feather, either. I find pinning the thing to a waistband to be uncomfortable, and don’t want to tear holes in my tshirts, blouses, flannel workshirts or sweaters (I’m usually in one of those). So I took a length of evenweave fabric ribbon I bought at Sajou during our Paris trip, designed a custom pattern and stitched up an alternate solution.
I doubt I will add other bits. I have a very elegant silver framed mini-magnifying glass. But it’s way too good and way to fragile to add to the rest. Plus I I don’t reach for it every time I sit down to work. I’d like to add the electronics tweezers I use when picking out, but there’s no easy way to modify them with a metal chain loop or bail for hanging. And I feel that the weight of the thing as is now is pretty much maxed out.
As to the utility of this portable toolset – I really like it. No more setting bits down on the table or chair arm beside me, then sweeping it off as I get up. I will still use my pirate lunchbox to carry the larger kit (more backup needles, my lint-trapping wad of silly putty, the magnifying glass, tweezers, more thread beyond the current skein-at-use, and the like), but for wandering around the house, sitting out on the porch or on the beach at the Cape, the chatelaine is all I need.
I even used it while we attended panels and readings at the Arisia science fiction convention in Cambridge, MA last weekend. And I don’t mind jingling like a belled cat as I wander around, although at Arisia I did wear a two-pocket workshirt, and stuffed the pin and its dangles into one of the pockets when we were in motion, mostly to keep the noise down, and to prevent anything from snagging on passers-by.
THE SYMMETRIES OF LINEAR STITCHED FILLS AND STRIPS
As promised here’s a rundown on pattern repeat type, and centering fills and strips in designated spaces on your project. For one, there’s really very little need to sit down and stitch-by-stitch completely graph out the design to your final dimensions. In general knowing where the edges and centers of your space, plus the pattern repeat type is all that’s required. These hints go for both fills in regular and irregular shapes, and for strip or band type designs that march along the width of your project, or decorate the edge of a garment.
And a note on grounds, if I may. Aida, Hardanger, Anne Cloth, and Monks Cloth are types of purpose woven grounds used for modern countwork. They feature prominent holes outlining their base size units. Departing from that established grid can be very difficult and involve piercing the fabric in the solid spots between the built-in holes. Partial stitches do exist in the purpose-woven world, and are much despised by stitchers. Working multiple grids skew to each other on the same piece of purpose woven ground is almost never done. I’d say never-never, but somewhere it might exist, although I haven’t seen it nor the rants of despair from folk who have encountered it.
Evenweave (or near-evenweave) is a bit more flexible. Since the stitchers count threads on evenweave instead of hole-defined units, they can employ multiple grids on one piece. If the stitcher decides to work their unit over 2×2 threads, two adjacent spaces can use different grids, offset by one thread so long as the juncture where they meet is taken into consideration. I did this on my Two Fish piece, using the skew alignment to hint at undulating motion. Note the knot and grid filling. Not only is it stitched discontinuously across the bel, I also interrupted the grid. Both sides are worked 2×2, but NOT on the same 2×2 grid – the tail section is displaced one thread up and over.

So when you see me talking about skew grids or using partial stitches when centering various types of symmetry on a single piece, please know that the ability to do this is mainly something that can be done on evenweave. Purpose woven grounds like Aida will limit the way patterns of differing symmetries can be centered against each other. It’s just a fact of life.
Before I begin, all of the fills and bands charted on this page are available in my Ensamplario Atlantio series, my Epic Fandom Stitch Along, or previously shared here on this blog. All are available as free downloads for personal use. Links are provided.
OK. Finally getting into it. Patterns can be grouped into a few basic clusters, with some caveats.
Center Line Repeats
First we have simple line-center repeats. These are designs that cover even numbers of units, and mirror along a center line. The chosen pattern may be a band or strip, with one vertical line where the design mirrors to its left and right. Or it might be an all-over design or fill, with at least one vertical and one horizontal mirroring line.
This blackwork fill/all-over design has both a horizontal and a vertical center line, marked in red. The motif tiles into square blocks of 14 units. The easiest way to use it is to either count to or (if irregular) eyeball the visual center of the space to be filled, then begin stitching the design at the spot where the two center lines meet. Even if the space to be filled is NOT a multiple of 14 but is any other even number of stitches, if centered this way the design will truncate neatly around the edges, as it does in the sample from Ensamplario Atlantio Volume 1, below.
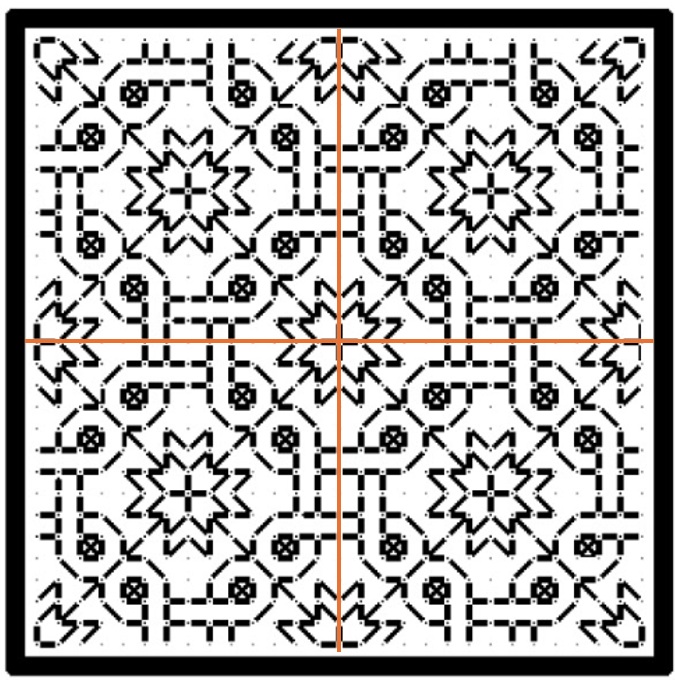
But if the space to be filled contains an odd number of stitches you will either have to displace the center lines so that there is one more unit to one side or the other, or you might have to work partial stitches all the way around the perimeter for full coverage.
Some people insist on using a single grid for ALL of the fills on an inhabited piece. That means that even if they are working over 2×2 threads on evenweave, where adapting the grid you are using to the space at hand would be quite easy, they choose not to. They end up having to either accept minor misalignments between adjacent patterns, or employing partial stitches to eke out the design. That can be avoided by NOT mixing fills or bands with this type of symmetry with some of those discussed later in this article.
Here’s the same type of symmetry expressed in a band pattern. This one is from my Epic Fandom Stitch Along. Note that in this simple meander there are two lines of symmetry (sometimes called mirror or bounce lines). The pattern replicates in mirror image on either side of them, just as it does in the all-over fill. One full repeat is 36 units, and alignment in your desired space can be focused on the center/mirror/bounce lines of either the up or down facing fronds.
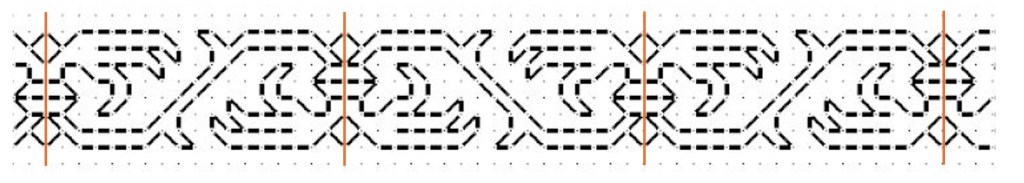
Regardless of symmetry type, if you are filling an irregular spot, and you are eyeballing the center alignment point you might end up having to work half stitches around the edge of your area, again to eke out the coverage. This is one reason why some instances of inhabited blackwork (the kind with the freehand drawn outlines infilled with counted geometrics) rely on heavily stitched, thick outlines. Those “fig leaf” the offending partial stitch spots and make the work look neater.
Here’s a bit on my Unstitched Coif, where I eyeballed the alignment of the fill, worked a ton of half stitches (a challenge on 72-74 count near evenweave, stitched over squares of two threads), then went back and put in heavier outlines to hide irregularities. Zoomed waaaaay in like this you can see them around the edges. For scale, that little bud at the upper left is smaller than a US penny.

Now there are some exceptions and complications. We’ll get to those later.
Center Unit Repeats
All well and good you say, but the symmetrical repeat I want to use doesn’t meet up neatly at a center line like those. In most cases your repeat has a “spine” of a single unit rather than a center line. That column or row of units is repeated only once, and is not mirrored, although the design itself does mirror left and right (or up and down) that non-repeating column or row. That means that a full repeat of the design includes two symmetrical wings, plus that pesky center unit – an odd number of units, total. Here’s a fill/all-over design that features center units. In this case one full repeat is a square of 23 units (one center unit, plus 11 more units to the left, and to the right of it).

And here’s a strip repeat, also with a simple center-unit style symmetry. Like the line unit band above, there are two possible centers. Either one can be used, although convention on band samplers is to feature two main motifs in the center of the stitched area – in this case the pair of beak to beak chickens.
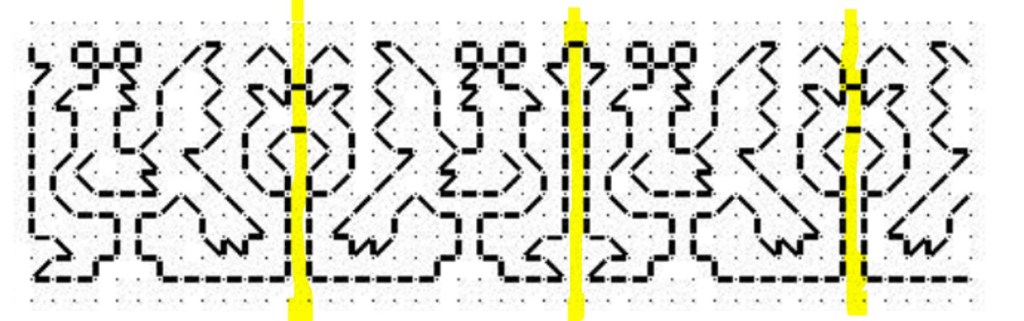
The strip above is from my Workshop Handout broadside, another free download here at String you can access via this post or via the Embroidery Patterns tab at the top of every page.
Hybrid Repeats
Some designs display a delightful flexibility when it comes to centering because they incorporate BOTH a center unit and a center line bounce point/mirroring. This happens with fills/all-overs and for strip/band patterns.
Here’s a sample of a fill that includes both. I’m only marking one repeat of each type on it, otherwise the thing will end up looking like a swatch of plaid.
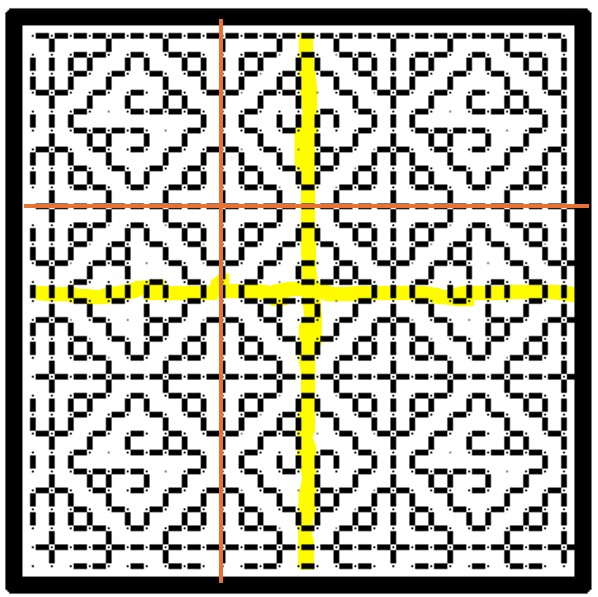
This design can be aligned either to the center lines (red), or center units (yellow). And here’s an example of the same type of pattern in a strip or band. The center can be the red line or one of the yellow columns.
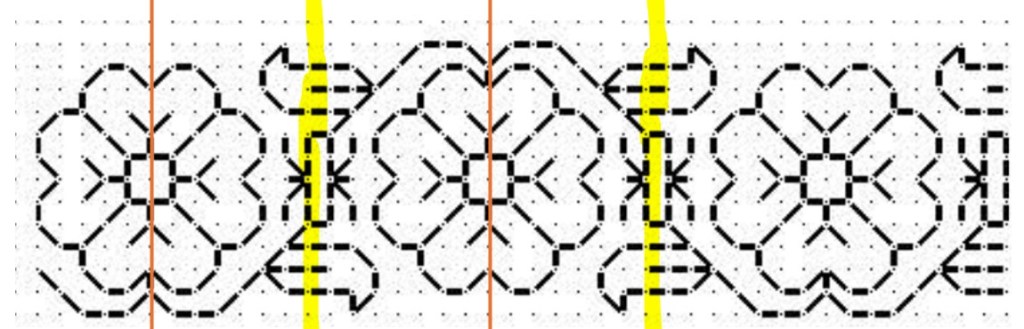
Again, if a combo of center line and center column symmetrical strips are used on a band sampler in a mixed environment that doesn’t deviate from one universal grid note that true center alignment will not be possible. The even-number repeat centerline bands will all line up with each other. But if you insert a design with center unit/column symmetry but have to use the same “stitch holes” in Aida as the rest of your project, that center column will not line up with the true center of the rest of the piece. Which may or may not matter to you. Food for thought.
Staggered Drop Repeats
Now it gets harder to identify these. This style of repeat is common in fills/all-overs, but less common in strips/bands, but they do occasionally pop up. For the most part they employ mini-motifs, sometimes in straight-on replication, sometimes with mirroring or rotation; and use regular offsets to place them. Sometimes its a simple half-drop, sometimes it’s a larger interval or not regular when the horizontal and vertical offsets are compared. Most of the time these staggered or evenly scattered mini-motifs do resolve into very large area true repeats, with the same motif repeating in the same relative position in the field, but it’s rare to use these in areas big enough for that resolution to happen. How to center them? It’s a bit more complicated.
Here are three with different rates of periodicity (how big the sample has to be before it manifests a true, full repeat), presenting different problems. These are all from Ensamplario Atlantio Volume 1, Second Edition.

The flowers at left can be centered in a panel in one of two ways. Either using the regular center-line symmetry of the very simple little four petaled flower, or by counting to identify the centerpoint of the more complex sprigged flower. Either way will work, although I think using the smaller mini-motif would be visually more pleasing. Note that regardless of the size or count of the space you use these repeats “walk” and will always truncate around the edges.
The snail garden square at the right is a hybrid. It can be effectively centered either on the tiny squares and on the larger snail-bearing unit. Both work nicely. Which I would choose would depend on the size of the space I wanted to fill with it. If the space was large enough to accommodate four of the snail gardens without truncation, I’d probably use the tiny squares as my center alignment point. The snail gardens rotate around them, and optically form a flower-like shape when viewed from a distance. If the space was small, I’d put the garden in the middle to ensure at least one full iteration of it was represented.
The griffin/dragon beastie in the center presents a harder problem. There’s only one element here, and it has no clear center line or center column/row. Additional complications come from the rotation and offset of the beastie motifs. The easiest way to center this one is to find the center point of the beastie itself, match that to the center point of the area to be filled, and work the others around the first, completing the truncated ones as possible. In the photo below, this is what I did with the wing like bits, second from the right in the photo below, and what I SHOULD have done with the little dolphins in the box next to them, but obviously didn’t.

The myriad mistakes in my current piece are what inspired this post. In addition to the errant dolphins in the latest section, you can see that the voided bit currently underway wasn’t properly aligned. It’s a center line repeat, I have an even number of units across, but if you compare the left and right edges, you’ll see that the design is shifted two units to the right. The center of that strip does not align with the center of the set of boxes, above. The dolphin box is intentionally shorted one unit compared to the others in its row because my count across is not divisible by four (available area minus 6 units total for the gutters between the boxes). There are more similar mistakes in the previously completed part, now wound around the roller bars of my stretcher frame.
I confess to making many alignment sins on this one that together have landed me in this predicament, including initially basting the center guideline that runs the entire length of the piece offset to the right by three units; never going back and measuring, but instead working the other vertical guidelines off that one; starting the first blocks and not bothering to confirm centers or edges until it was too late to pick out and start again; fudging everything in to try to compensate for the pile of errors that was accumulating behind me; and not paying enough attention to centering the various fills in their boxes.
I will continue on to completion with this one, warts and all, but I may revisit the base concept of voided strips alternating with boxed fills in a future work.
ANOTHER NEW TOY
If you’ve been reading here over the past month, you’ll have seen me working the current project in a hand held hoop. I love hoops, especially their portability and versatility. But I vastly prefer the “real estate,” tautness, and ability to use two hands that using a scrolling frame gives. I’ve had two sizes of the Needle Needs Millennium frame for quite a while. I tend to pull those out for the big projects, especially those with metal threads, or that feature easily crushed or disarranged stitches (satin stitch, knot stitches). I also have a sit-upon hoop. I do use that extensively for the smaller pieces with less fragile work on them. It has some of the advantages of the other two types, but as a compromise, with less ability to place the piece in exactly the optimal spot and angle for visual acuity and best lighting. The hands down most efficient way for me to stitch is the big Millennium on my Lowery stand.
After months of hoop-in-hand, I was yearning for the scroll frame experience. I heard that Needle Needs had a new junior size frame, and was also offering smaller roller bar and side extension pieces for the Millennium system. So I sat down and weighed price, stitched area size, and the fact that pieces from the new junior frame are not compatible with its larger brother, then splurged on a pair of new extenders and roller bars.
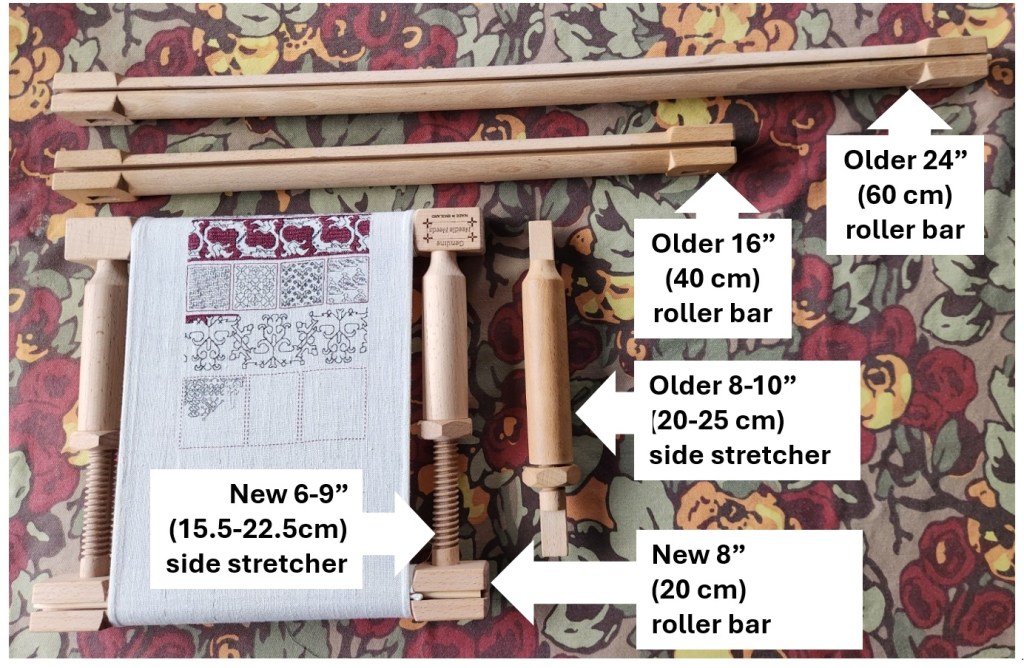
I have two sets of the older 8-10″ side stretchers. I got that relatively small size because I realized that the bigger ones would produce a stitching area that would be difficult to reach. That bore out when I was working the coif using the 24″ roller bars and the 8-10″ extenders. My behind-the-work left arm could reach only 60% of the available area with it set at full extension – barely making it to the top edge of my piece, and I had to flip the frame over to work the remaining spaces. But while I might have gotten the even smaller 5-7″ sides this time around, I had the feeling that a space that small in combo with the Lowery frame extender arm would be less than optimal.
Obviously the new components arrived yesterday and were immediately deployed:

And I was right. You can see how much of the available area is “eaten” by the width of the gripping Large Frame Extender. Even if I position the frame so that the clamp is grasping the corners of the roller bars, it’s awkward to work right up against the Extender’s upright. But just like with the larger set-up for the Coif, I can flip the frame upside down to work that side of the piece.
I know that not all my new projects will be narrow band samplers, but between the new short roller, and the new short side stretchers, plus the pieces I have on hand used in new size mix combos, my toolkit has valuable extended capability.
As for more on the design on this sampler, the types of symmetry often seen in fills and how to best center them depending on the type of symmetry, that will have to wait until the next post. For some reason the blogging software is having indigestion, and I’ll have to cut today’s intended post into two. Will finish that one out and get it up by the end of the week.
TALKING HOOPS AROUND THE SUBJECT
Yesterday was a needlework housekeeping day. I put away the supplies from my last project, neatened up my stitching-on-the-go box, and cast an eye over my kit in advance of whatever project I will do next. And there WILL be a next – it’s just a matter of getting a couple of holiday obligations finished first.
Among the reassessments I made was an evaluation of my hoops. I have several. My best ones are three in-hand hoops, and one sit-upon hoop on a stick. All are hardwood wood and better quality, with sturdy brass hardware – not the bamboo ones with fragile clasps. Three of them are shown in the family photo below. The other one is an unwrapped duplicate of the smallest, shallowest hoop. I haven’t wrapped it because it happens to have much better tension than the one I did wrap, and there might be call for me to use an unwrapped hoop for a specific purpose. Since I don’t leave my projects hooped when dormant, there’s no call for me to have two absolutely identical ones, both prepped and ready.
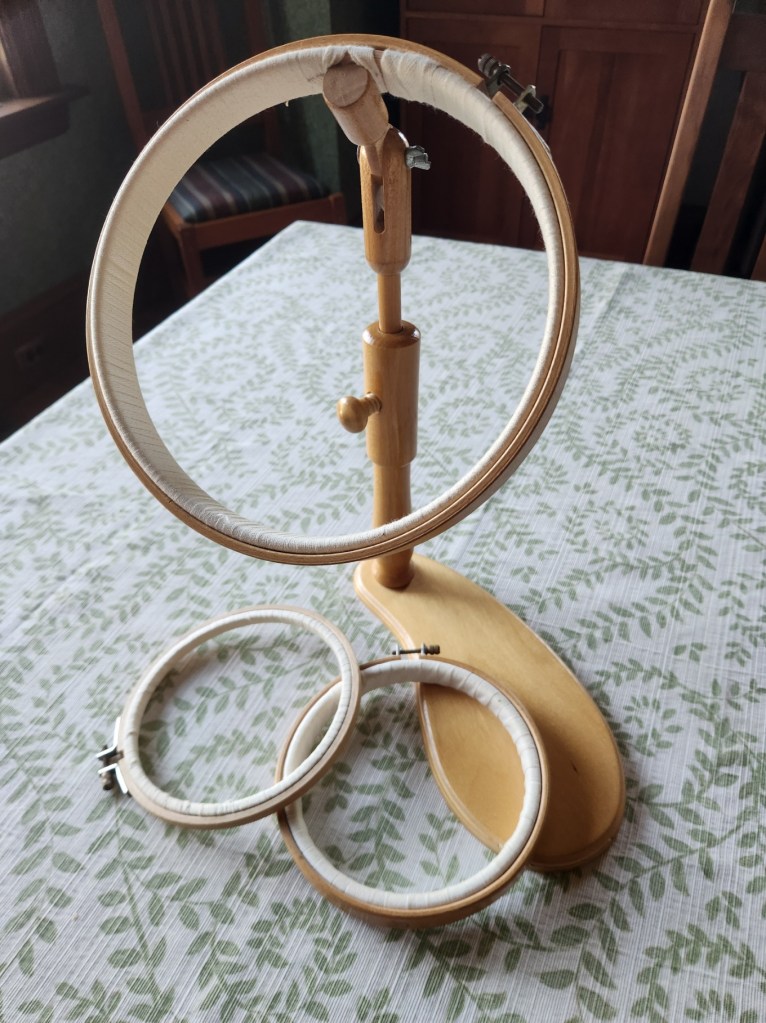

The in-hand hoops are all 6 inches (15.24 cm) in diameter measured across the inner hoop. I find that the most convenient size both for maintaining tension and for use in tight places. The sit-upon is 8.75 inches (22.22 cm) across the inner hoop. I note that a 6 inch diameter hoop/stick part is now available from the maker. I might pop for that someday.
The ring of one of the in-hand hoops is 1/4 inch (0.63 cm) deep, and the other hand held one is 5/8 inch (1.59 cm) deep. The hoop on a stick is even wider – 7/8 inch (2.22 cm).

I also have a selection of both plastic and wooden quilting size hoops, a foot in diameter or more that I’ve gotten as hand-me-downs, or as part of “take the lot” yard sale/jumble sale needlework bundles. I rarely use them because I find they are cumbersome, and they don’t provide the drum-tight tension I prefer. None of those have been promoted to my on-deck group, and aren’t shown.
But why so many of the smaller diameter? Well, it happens I do have several larger scrolling frames, and use them when needed – mostly for things that have fragile threads, metallic threads, or other raised embellishments; or that employ crush-prone stitches that a hoop could injure when it is repositioned. But for smaller pieces, non-fragile pieces, and in some cases REALLY big projects like tablecloths, I prefer the hoops. These days I mostly use the sit-upon, but for sitting on the beach and stitching, the sit-upon is useless. You can’t sit upon a hard paddle seat in a soft fabric sling chair – so hand hoop it is.
Why both the deep and the shallow? The deep ones (including the hoop on the stick here) work better with thinner fabrics – the 38 and over count linens and blends I usually use. The shallower ones work better for thicker fabrics, especially heavy 28 to 36 count evenweave, denim, and other sturdier fabrics. If I used most Aida I’d probably employ the shallower hoop for that, too. Do you have a standard deeper hoop and you are struggling to get it over your Aida? Try a thinner wall hoop. It will be easier, even if you wrap the hoop.
Wrap the hoop?
Yup. Makes a world of difference. Wrapping the inner hoop with 100% cotton twill tape vastly improves the grip of the thing, and makes the fabric much easier to mount and to tension. It also cushions the work a bit, cutting down on stitches being crushed. I will probably wrap the outer hoops, too, to prevent those shiny areas that happen when densely packed stitching meets hoop tension. But so far I haven’t bothered.
How to do it. Note that the deeper hand-held hoop is wound with wider twill tape than the other two. That was the first one I wrapped. I have to say it was significantly harder to do it with the 3/4 inch (1.9 cm) tape than it was to do with the 3/8ths inch (0.95 cm) tape. The narrower stuff is easier to stretch to conform to the circle of the hoop, without lumping and gapping.
Lumping and gapping on the outer edge of the inner hoop is to be strenuously avoided. That leads to high and low spots with suboptimal tension. The inner surface can be less “policed” but it shouldn’t present gaps or kinks that might work their way around to the top, or catch needles during stitching.
I find the best way to achieve as uniform a contact surface as possible is to overlap the tape by 50%, row on row, and wrap as tightly as possible, maintaining the established angle and stretching the tape as I go. Yes, it can take me a couple of tries before I hit on the angle that produces the most even results.
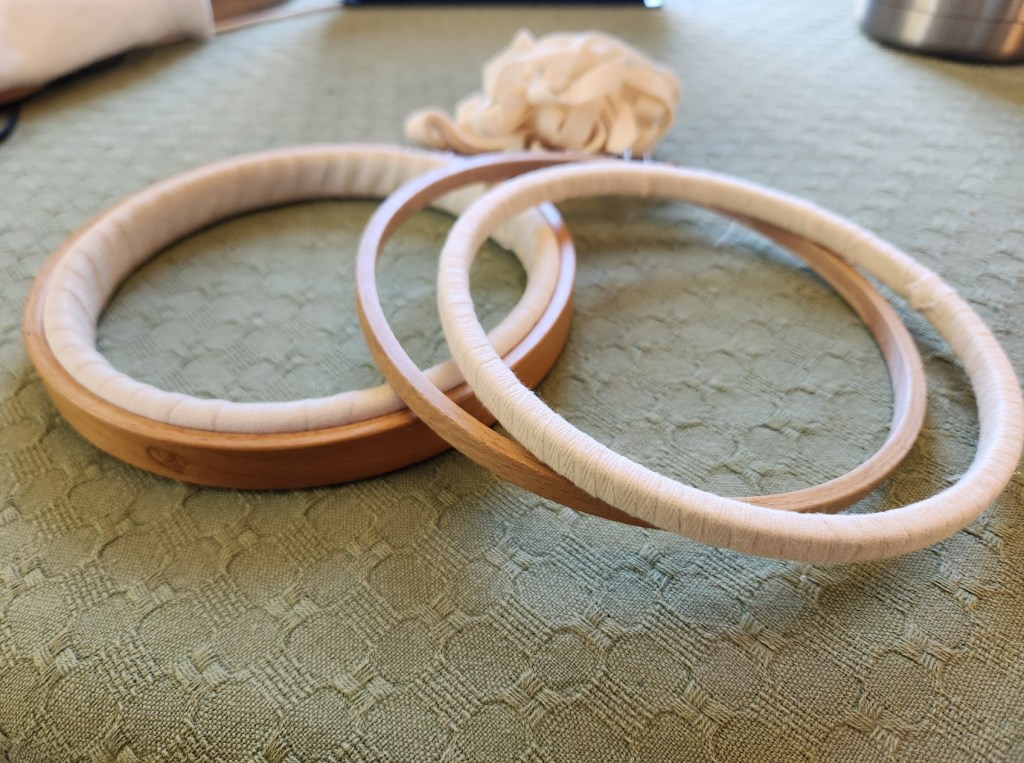



I don’t use glue or tacks to hold the end, I just wrap, gripping the tape and hoop very tightly, placing each successive course with special attention. Here you see the start and the midway point. Eventually the origin end will work itself a tiny bit loose as I go, but I keep it folded flush against the inner surface of the ring, and take care to wrap over it. Eventually I get back to the start. I cut the tape, tuck the ends under to prevent fraying and firmly sew it to the inside surface of the ring, back where it meets the beginning. That spot is indicated by the arrow, below.

The only caveat on this whole thing is that wrapping may add so much diameter to the inside hoop that the little thumb screw holding the clasp together becomes too short. This happens mostly on the less expensive/mass market type hoops. If that happens, a quick stop at an old fashioned hardware store can help you land a longer replacement. And by that I mean a store with actual people who know the inventory, not a big box/self-serve hardware department store that sells everything in quantity, entombed in blister packs. Bring the hoop and screw in and explain the problem at a non-busy time. The staff will be able to size it and find **just** the right thing.
And that’s how it’s done. If done with proper care, wrapping a hoop of this size takes me about a half hour. And a half hour well spent.
Other Recent Projects
The multicolor headscarf I was stitching has finally been made up into its finished form – a lined triangle with ties. The ties are also 3/8 inch twill tape, but a heavier/denser and whiter one than that used on these hoops. I folded it in half longitudinally and stitched it to make robust tie strings. But I didn’t remember to take a finished item photo, and then decided to give it as a present to a dear old friend who married over the weekend past. I forgot to ask permission to use a photo of her wearing it. But I am happy that she loves it enough to tie it on immediately after the ceremony.
And the Fractured Symmetry sampler joins the rest of the to-be-framed or finished works on my Wall of Shame.

He is tucked in next to the underskirt panel at the far left, just below Stone by Stone. In addition to some of my perpetual unfinished objects (UFOs), there are now six pieces there, stitch complete, waiting for framing or other finishing. I suppose I should get on that.
BUT in the mean time I have seasonal obligations to meet. I promised a stocking with a wolf on it before the holidays hit. I’m on it. The recipient’s name with be duplicate stitched into the white band at the top. I’m afraid that the distortion inherent in translating squared graphs to rectangular knitted stitches (wider than they are tall) has stretched poor Wolfie a bit. I am hoping that additional embroidery – maybe an eye and some ornaments on that tree, will make him both more identifiable and more festive.

The pattern is one I’ve done twice before, once for each of the spawn. But the last time I knit it was 25 years ago. I found one of the pattern pages, but not the others. I’m extrapolating from the other two extant stockings. An interesting exercise, for sure.

LETTERS FROM THE PAST
Antipodean social media pen pal and long time needlework/knitting co-conspirator Sarah Bradberry recently posted about a thrift store find – a 1971 vintage book entitled Lettering for Embroidery. It’s available for borrowing at the Internet Archive (free account sign-in is required). It’s an interesting read, although its overall aesthetic now looks 60s-retro rather than cutting edge fresh. Which is to say that it’s back in style.
Her post made me think about some of the unconventional alphabets I’ve drawn upon for my various non-traditional samplers, why I picked them, and how I used them.
To begin, I like letter forms – perhaps an inheritance from my grandfather Mack who owned a printing company. He would point out the often tiny differences among various typefaces and font sizes in printers’ samples, advertising materials, newspapers, and in books, and how those differences contributed to the overall message of the printed piece. While I obviously didn’t follow him into the family business, some of what he showed me must have stuck.
Let’s start with one of the more outrageous. It’s a phrase in an non-Terran language, picked up from my one of my Resident Male’s writing ventures. The book itself isn’t out yet, but I can say that in the text, it is translated as “Life’ll kill you.”


Ringed with my dancing skeletons, and bedizened with sword bearing interlaces to echo the stated meaning, I wanted to use an almost unreadable other-worldly set of letter forms; shapes that themselves danced. I went to my go-to spot for graphed alphabets – the free Patternmaker Charts collection of antique Sajou, Alexandre, and other leaflets. This one is from the Rouyer #248 booklet. I kerned and leaded the rather large letters tightly, to accentuate the flow of the curls across the words. (Kerning is the space between letters, leading is the space between lines of type). In terms of composition, the three words are centered, with no regard for how the letters stack vertically. These letters are also proportionally spaced because they vary so much in width, and cannot be easily worked monospaced (the way an old fashioned fixed-width Courier typewriter prints.)
Here’s another where I tried to fit form to the statement. The full chart for Don’t Panic is free here on String.


Yes, I know in the Hitchhikers’ Guide books the phrase is described as being “in large, friendly letters,” but this was going into my office where I managed frantic people wrestling deadlines under extreme pressure. I thought a jittery sign would be funnier. My favorite source to the rescue, this alphabet is from Sajou #325. It drips nervousness, even though the firm serifs imply regular stability.
Note that as with many of these vintage alphabets, the letters I and W are omitted, in keeping with the paradigm of classical calligraphy. I extrapolated the I, and doodled a matching apostrophe. Again, I kerned tightly, although I’m not fond of the space between the A and the N. I should have tucked them closer together, as I did between the P and the A. But As are problematic. I also chose not to center these words one on top of the other. The offset adds to the perceived unease.
Here are two more (slideshow presentation to save space, click on arrows beside the photo to advance). In these I chose to use the words as horizontal bands of ornament, flush left and breaking words when I ran out of space. I went back and eked out the bands to come up to the right margins. Mostly I did this because I was impatient. I didn’t want to take the time to do a full arrangement of the motto as it would appear before working the rest of the piece. I knew I’d have space to work the full quotation, but just stitched them letter by letter, with no advance planning. Since I had seen historical samplers that did just that, I felt confident beginning flush left and cutting words in the middle as space dictated.
I am not sure where I got the alphabet for the “Do not meddle in the affairs of wizards” piece. I stitched it circa 1994/1995, just before I began keeping a blog. Obviously the source followed the additional classical convention of presenting just a V shape to cover both that letter and U. I’m also pretty sure I extrapolated the I. In any case, the thread count on this one is no where near as fine as on the others above. There was less room for larger lettering, and I had to find something small enough to fit (most of) the words in, with minimal truncation.
The Arthur C. Clark quotation uses another alphabet from the Patternmaker collection, this time from Sajou #55. It may even be the project on which I stumbled across that source. Being a two-color piece, I wanted something that combined both, and that had an old-fashioned, formal look without being very stuffy. The red swirls suggested a bit of obfuscation and incantation as they tendril around the more solid letter forms. Again I extrapolated the I (thankfully there are no Ws in the phrase). This alphabet with the exception of the I has a very blocky, chunky and solid appearance in spite of the red whisps. There was no need to play with kerning, and spacing between words was easy and regular. The general look of boxy solidity underscores the sentiment expressed. For the A.C. Clarke attribution, I was lucky to find a tall and narrow alphabet in Sajou #172 to fit remaining space on the final lettering line. I will say that after this piece I lost my appetite for broken words.
At the risk of alienating all, my two coarse language pieces (behind the eyeball fig leaf image, also in slide show) use formal typefaces to express very informal and direct sentiments. If you are easily offended by rude words, skip ahead.
The Covid sentiment, done in a blackletter typeface, uses two alphabets from a German book, available on Patternmaker Charts. One is uppercase, the other lower. The lower case alphabet also supplied the numbers. Again I had to invent a matching letter I. Blackletter family typefaces are reserved for formal documents like diplomas, and newspaper mastheads here in the US. I wanted to play on that gravitas.
Similarly, for the admonition done in green, I wanted to evoke the greeting card world of hearts and gentle sentiment, to contrast the general scolding represented with sweetness and light. I picked one of the flowery alphabets from Patternmaker Chart’s Sajou #160 but leavened it with a smaller yet still uppercase typeface for the rest of the lettering. That classic form serif alphabet is from Grow and McGrail’s Creating Historic Samplers. The R of Remember is from Sajou #1 also on Patternmaker Charts, and the lower case lettering for the rest of that word can also be found in the Grow and McGrail book. I also adapted the floral ornaments from the initial letters for use as fill to surround the lower case one.
Pay Attention to Trifles has the most typefaces I’ve ever used on a single piece. I wanted the word Attention to leap out, Trifles to be the most ornate, and the message to be decoded only on a second glance. And I wanted a vaguely carnival type over the top mix of styles to complement the extremely busy design that is stuffed full of buried “Easter Eggs” as requested by the recipient.

All of these are from the Patternmaker Charts website.
- Pay – Sajou #652
- Attention – Sajou #654
- Even to – Alexandre #143
- Trifles – Sajou # 53 and 203
The dual tone coloration on these was not always noted in the original. Some I tarted up myself. I kerned each line separately, trying to best suit the alphabets being used, squishing ATTENTION a bit made it shout louder. Letting the other lines straggle a bit more made them a bit more lyrical.
While busy, the mad assortment is just over the top enough to gentle the nagging advice of the motto. If I had done the entire thing in the same face as Attention, the statement would have been way to strident. Throw in a bit of whimsey and it becomes an in-joke between the donor and the recipient. The centered text with the balanced motifs left and right is in contrast to the rather chaotic jumble of gears done in inhabited blackwork. There is repeating arrangement of the gears (more or less), but not the strict centering of the lettering. I think that adds to the haphazard playfulness of this piece.
I have done lots of other pieces with mottoes or words on them, but they don’t really showcase different approaches. The last one I’ll cite here is the piece on which I’m currently working. I’m almost done with the penultimate band, and have designed another custom-fit to go below it and end off the work as a whole.
I can’t say for sure where I found the alphabet I modified for use on this one. I found the image in my notes folder, with no attribution other than mid-March 2020 save date. I ended up upscaling from the typeface as charted by using a block of four units for every single unit in the original, and smoothing angles accordingly. Using the squared fill for the shadowing was intended to make the text reminiscent of a brick wall. That the span of the words is larger than the rest of the piece and contributes to that effect is serendipity, not planning. My count was off, and (thankfully) having started in the center, at least the motto protrudes mostly evenly left and right, looking even more monumental than I had planned.

I did kern aggressively to make the motto fit the space, but I should have lost one more unit between the B and Y of by. Still, I think it works. It’s blocky, yet because the letters are represented by outline and shadow, it contrasts nicely with the rest of the piece, overrun as it is with very busy fills.
OK. A conclusion now. Sort of.
If you are designing your own motto bearing piece, there are lots of choices out there that can make a real impact on the design, above and beyond the decorative elements that surround it. If you are unburdened by time/place restrictions (you are not designing a piece in the style of a specific location, school, style, or era), you are free to play. Think of the lettering as another element you can manipulate to underscore the message of your motto, or to convey a mood in which you would like it to be received.
Want to be playfully threatening, like an admonition to keep the kitchen or bathroom clean? How about using a different typeface and font size for each letter, to make it look like a ransom note. Want to convey warm wishes and affection to your extremely sweet and caring (but possibly somewhat humorless) family member? How about one of the ornate flower-bedecked alphabets from around 1900? Have a Goth leaning pal whose heart beats for irony and sarcasm? Use that same flower font in funereal black and purple to express an over the top sentiment.
You can speak words with typeface choice, font size, color, and spacing beyond the actual ones you stitch.
MUSEUM DISPLAY OF CROSS STITCH WITH ART
This week past we were in the Buffalo, New York area, visiting family and friends. We had a splendid time, and one of the things we did was pop over to the newly expanded and refurbished Albright Knox Gallery of Art, in the Delaware Park section of Buffalo. The museum itself is a little jewel box of contemporary art, with a surprisingly comprehensive sampling of works by most of the 20th century’s biggest names. Now it has the room to better display its collection, and additional space to stage specialty exhibits.
Right now they are offering After the Sun – Forecasts from the North – a collection of works by contemporary artists from the greater Scandinavian/Nordic/Icelandic sphere, as they contemplate the effects of climate change on the northern/Polar bordering landscapes and society. The works were done in many media, everything from traditional oil paint on canvas and carved wood/stone or cast sculpture, to stretched scraped membranes, and even a presentation of scented oil. And to my surprise it included a suite of cross stitched pieces. While it’s not uncommon for embroidery to be displayed in a museum, it is more usual for it to be seen by itself, and not as common for it to be displayed alongside other pieces outside of a historical context (like a “life in the 1500s” type exhibit). This was a general arts collection, with the stitched pieces being given the same respect of place as those done in more represented media.
The items below were composed and stitched by artist Vidha Saumya, a resident of Helsinki, with roots in India. Her exhibit’s blurb is below. I wasn’t able to get detailed shots of all of the pieces, but they are shown after the blurb.

Pieces 1-4

A close-up of #4 – Still the Day May Live. I apologize for the skewed perspective. These were hung both above and below eye level, making it difficult to grab a photo.

Pieces 5-7

And Pieces 8-11

Again I apologize for the poor photos.
I don’t pretend to be an art critic (especially not of non-representational art) but I was moved by these. They seemed both immediate and unspecific in time – like dream images barely remembered upon waking, inhabited by an overlay of dread and nostalgia, with flecks of wishful joy.
I want to express appreciation for the curators of this collection, and I wish Ms. Saumya every success. I was very happy to see the medium both given respect, and being used to such good effect.
ELIZABETH HARDWICK ON BIAS?
Once again a chance image on Facebook throws me into a frenzy of charting. The Friends of Sheffield Manor group posted this image of Elizabeth Hardwick, Countess of Shrewsberry. attributed to the school of Hans Elworth. It’s accession 1129165 of the UK’s National Trust collection.

Obviously what struck me were the sleeves. I tried and tried to chart them on the diagonal, but the geometry worked out much more cleanly if done straight. Now sewing, especially historically accurate construction is not my strength. But I ask folk more versed in it than I am, was it possible that if embroidered linen was used for those sleeves might they have been cut on the bias and not with the grain? The motifs look grain-wise at the collar, but are clearly sitting “on point” on the diagonal for the sleeves.
In any case, I’ve added the graph to the on-site free collection here. My rendition of it is approximate, but as close as I was able to achieve. I’m fuzzy on the exact shape of the free floating rondels occupying the empty areas where the chain rosettes meet. And their color is also problematic. Some are brown, some red, and some a pale indeterminant color – it might just be fading of the paint.

I lay no claim to the design itself – only my graphed rendition. Like most of the pieces offered here on String, this is available for your personal use. It’s Good Deed Ware – if you work it up please consider paying the kindness forward, assisting someone in need, calling a friend or family member who could use a bit of cheering up, or otherwise making the world a tiny bit more pleasant. And please note that my representation of this design is copyrighted. if you are interested in using it commercially or for larger distribution, either incorporating it into a pattern for sale or other dissemination, or if you want to use it on items that are made for sale or donation, please contact me.
And as always, I love to see what mischief the pattern children are up to out there in the wide-wide world. Feel free to send me a photo or a link. And if you give permission, I’ll add your work with or without your name (as you desire) to the growing Gallery page here on String.
A SUPPORTING CAST OF GRIFFINS
Friend Craig posted a memory last week, and re-shared a chart he adapted from one of the Siebmacher modelbooks – from the 1611 edition.

It got me to thinking. Those heraldic style charted bands appear over many years, and in several iterations. It might be fun to see how they assorted over time. So I went hunting. I combed through my notes, the Internet Archive’s collection of modelbook images, and several other sources.
This isn’t an exhaustive analysis, but it covers most of the easily accessible editions of the chart. And the large number unearthed really underscores the differences in that accessibility from the time I started poking into these early publications (circa 1974) to today. Back then there might be a couple of modelbooks as part of a microfiched set of early publications on file at one’s university. There were several sets of these ‘fiches scattered across the country, so the set that was local to me at Brandeis wasn’t necessarily the same as the set someone else might have at the University of Pennsylvania. A happy trade of blurry low quality photocopies ensued among us needlework dilettantes, and in some cases precision in attribution wasn’t as clear as it could have been. As a result, when I get around to reissuing The New Carolingian Modelbook, my first book of researched patterns, there will be corrections. Especially among the Siebmacher attributions, because somewhere along the way prints from several editions became confused, leading to a couple of the designs marked as being from the 1597 edition, actually being from a later printing.
And Siebmacher or Sibmacher – both actually. I haven’t a clue as to which spelling is the correct one, because both are used. IE is represented more often than just I, so I go with that.
So here we go. It’s another overly long post only a needlework nerd will love.
1597
Johann Siebmacher’s Schon Neues Modelbuch von allerley lustigen Modeln naczunehen, zuwürcken unn zusticken, gemacht im Jar Ch. 1597. Printed in Nurmburg.
This edition is held by the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Accession 20.16 and can be accessed here. Notes accompanying this edition cite that the modelbook historian Arthur Lotz cataloged two editions were printed in 1597, and this is from the later of the two. (I will try to fill in the Lotz numbers for these as I mention them. I have that book, but I don’t read German so please forgive my tentative attributions.) My guess is that this one is from Lotz 32b.
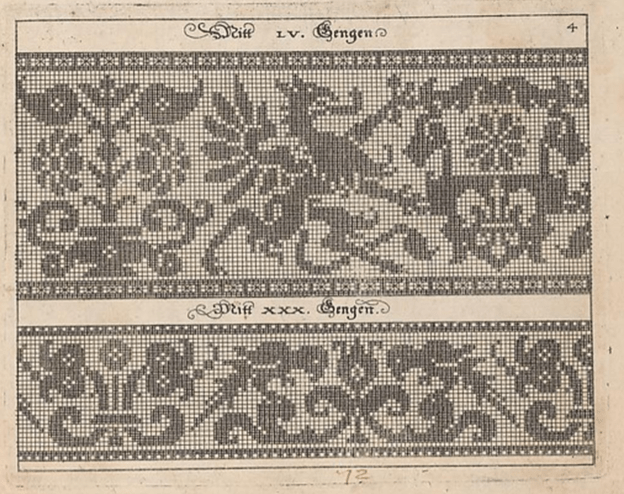
Note that it presented on the same page as the parrot strip. The numeral LV (55) at the top refers to the number of units tall the strip is. Note that all filled blocks are depicted in the same way – as being inhabited by little + symbols. There is also a companion border that shows a combo of filled boxes and straight stitches. Also note that the two “reflection points of the repeat are both shown, along with enough of the repeat reversed to indicate that the design should be worked mirrored. Craig got this spot on when he drafted the design for himself. I’m used to working straight from the historical charts but most folk find the mental flip a bit arduous. He wisely spared himself the conceptual gymnastics.
Johann Siebmacher’s Schon Neues Modelbuch von allerley lustigen Modeln naczunehen, zuwürcken unn zusticken, gemacht im Jar Ch. 1597. Printed in Nurmberg.
Here is the same page from the other edition of 1597. Very possibly Lotz 32a. It’s held by the Bayerische Stasts Bibliothek, and is shared on line here.

It’s very clear that these are both impressions from the same block. The inking is a bit heavier on this one than the other, but the design is the same. Note though that the little “4” in the upper right corner isn’t shown on this one.
The Bibliotheque nationale de France’s copy of Johann Siebmacher’s Schön Neues Modelbuch von allerley lustigen Mödeln naczunehen, zuwürcken unn zusticken : gemacht im Jar Ch. 1597 looks like it might be the same printing as the Lotz 32b version above. It has the same “4” in the corner. BUT throughout the book it appears that someone has added shadings and color variation indicators by hand – over-inking or penciling in selected areas of many of the patterns. I don’t know if this was done by an owner, or was sold this way. I suspect the former. The darker boxes are clearly produced by careful inking, not printing. In other pages of this edition, you can see differences in how thick the ink was laid on, following pen or brush stroke lines, and not imprinted.

I don’t see a date associated with this other annotated edition, listed only as Johann Siebmacher, Newes Modelbuch, but I suspect it’s the 1597 one based on plate similarities. It’s another book in the Clark Art Institute library. Again someone took the liberty of hand-inking some of the pattern pages to add additional shading or interest. You can view it here. Given the placement of the shading, it might be the source for the version Carl used when he drew up his own graph.

Additional reprintings.
I’ll spare you more echoes of exactly the same page, but here are other representations of these 1597 editions.
There was a reproduction made in 1877, called Hans Sibmacher’s Stick- und spitzen-musterbuch: Mit einem vorworte, titelblatt und 35 musterblattern. The editor was Gerold Wien, and it was put out by the Museum fur Kunst und Industrie. The plate is a duplicate of the Lotz 32b one, complete with the 4 in the upper corner. The date of the original is cited in the repro. You can see it here. A second copy of the 1877 facsimile edition is held by the Bayerische Staatsbibliothek and can be found here.
There is an additional reproduction of this book in the collection of the Cleveland Museum of Art, as issued in Berlin in 1885. The image quality is excellent, you can find it here.
1599
Martin Jost. Schön Neues Modelbuch von allerley lustigen Mödeln naazunehen Zuwürken vn[d] Zusticke[n]: gemacht im Jar Ch: 1599. Printed in Basel.
Yes, a different name is on this book. Lotz 34 refers to it by the name of the publisher – Ludwig Konig in Basel. The on line listing also mentions Jost. It is very closely related to the works above with lots of designs in common. But not entirely the same. The on line copy is here.

That’s our friend the griffin, the same motifs on the shield being supported, and the same flower pot behind – all absolutely stitch for stitch true to the earlier version. But the repeat is truncated along the left edge. The left side of the flowerpot is gone. However the upper and lower companion border with its straight stitching is the same, and is aligned the same way with the main motif. Obviously the parrots are gone, replaced with a panel representative of cutwork. The words above the design are the same font size and typeface, but are now centered between the new borders. The letters have the same proportional size to the design’s block units, but the block units are now rendered as solid – not boxed crosses. These books are said to be among the first created using copperplate – not carved wood. I am not familiar with the process of creating those, but it does look like a print of the original might have been used to create this smaller version. Licensed reproduction, cooperative venture, or unauthorized knock-off? I am sure there are academics who have explored this, so I won’t let my speculation run wild.
Additional appearances.
There is another copy of this same griffin imprint in a book cited as Ludwig Kunigs Fewrnew Modelbuch, von allerhandt künstlicher Arbeidt: namlich gestrickt, aussgezogen, aussgeschhnitten, gewiefflet, gestickt, gewirckt, und geneyt : von Wollen, Garn, Faden, oder Seyden : auff der Laden, und sonderlich auff der Ramen : Jetzt erstmals in Teutschlandt an Tag gebracht, zu Ehren und Glücklicher Zeitvertreibung allen dugendsamer Frawen, und Jungfrawen, Nächerinen, auch allen andern, so lust zu solcher künstlicher Arbeit haben, sehr dienstlich. Printed in Basel, 1599. You can find it here.
The Lotz number for this one is 35. It’s a problematic work because it looks like at some point a bunch of pages from several different pattern books were bound together into a “Franken-edition” incorporating some of Pagano, Vincoiolo, and Vecellio in addition to the Siebmacher-derived pages. But the solid blocks griffin with the cut off flower vase, plus the cutwork panel below is identical to the other 1599 imprint.
Jost might have been a bit peripatetic. There is an identical impression of this version in another Jost Martin printing, Schön neues Modelbuch von allerley lustigen Mödeln nachzunehen, zuwürcken un[n] zusticke[n], gemacht im Jar Chr: 1599, printed in Strassburg. No differences from the one above, so I won’t repeat. Possibly the same Lotz number, too. But you can visit it if you like.
1601
Georg Beatus, Schon neues Modelbuch, printed in Frankfurt, 1601.
Yup. Another publisher. This copy is Lotz #40, and is held in the Clark Art Institute Library. You can see it here.

This print looks a lot like the Jost/Konig one, but not exactly so. First, you can dismiss those little white dots. Those are pinpricks, added by someone who ticked off the solid units as they counted. I deduce that because they are also present in many of the empty boxes. But you will notice some oddities. First, the design is further truncated at the right. We’ve lost the complete shield shape bearing the quaternary flower. And the column at the far left has been duplicated. There is also an imprecision on column and row width in this representation, absent on the others. Finally, it’s been formatted for a single print, with no supplemental design below. I’m guessing another plate.
1604
Johann Siebmacher. Newes Modelbuch in Kupffer gemacht, darinen aller hand Arth newer Model von dun, mittel vnd dick aussgeschneidener Arbeit auch andern kunstlichen Neh werck zu gebrauchen. Printed in Nurmberg, in 1604, in the shop of Balthasar Caimox. It’s in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, accession 29.59.3, and can be seen here. I don’t see this one listed in Lotz under 1604, but the Met’s listing says that it’s likely a re-issue of the 1602 edition which would make it one of the ones Lotz labels as 38a through 38e. What’s notable about this particular copy is that while many of the other fabulous animal/mythical creature strips that accompany the griffins page in the other works, the griffin page itself is missing. It wasn’t in this edition, or the page that bore it has been lost to time. I’ve included this citation here for the sake of completeness.
Note also that this 1604 edition is the one upon which the modern Dover reprint is based. Dover reissued Ernst Wasmuth’s 1880 publication, which he entitled Kreuzstich-Muster 36 Tafeln der Ausgabe v. 1604. That was based on 36 plates from this 1604 printing.
1607
Sigmund Latomus, Schön newes Modelbuch, Von hundert vnd achtzig schönen kunstreichen vnd gerechten Modeln, Teutsche vnd Welsche, welche auff mancherley Art konnen geneet werden, als mit Zopffnath, Creutz vnnd Judenstich, auch auff Laden zu wircken : Dessgleichen von ausserlesenen Zinnigen oder Spitzen. Allen Seydenstickern, Modelwirckerin, Naderin, vnd solcher Arbeitgefiissenen Weibsbildern sehr dienstlich, vnd zu andern Mustern anleytlich vnd verstendig. Printed in Frankfurt, 1607.
Yes, another name on the spine, and printed in another city. The copy from the National Library of Sweden is visible here. It’s cited as being Lotz 43b.
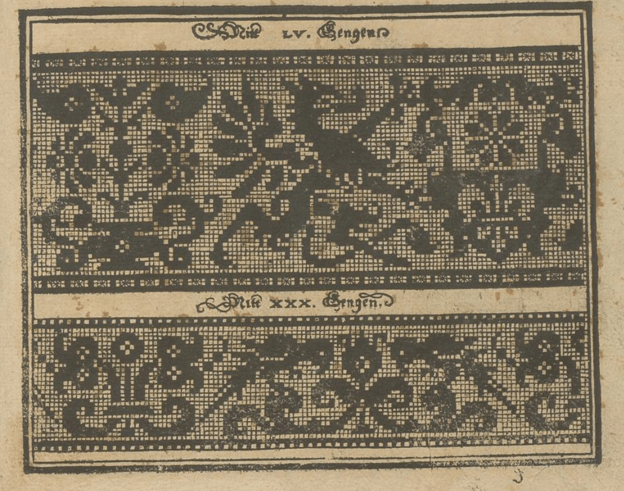
At first glance this looks like another imprint of the same Siebmacher griffins and parrots page from 1597, but look closer. This design adds a blank column of squares to the right edge, replacing the design elements that were there on the earlier block. This is especially evident in the parrot strip, which has lost its center reflection point along the right edge. Also the blocks are filled in, again not the boxed crosses of the earlier work. And the fills look printed, not applied (more on this later). Yet another plate? Not impossible.
1622
Sigismund Latomus was still active in 1622, issuing a modelbook, entitled Schön newes Modelbuch, von 540. schönen auszerwehlten Künstlichen, so wol Italiänischen, Französischen, Ni-derländischen, Engelländischen, als Teutschen Mödeln, in Frankfurt. As one would expect from the lengthy name, he swept up a number of pattern images, issuing them in one big bundle. Of course we can’t rule out that what we see isn’t the original document as published. It’s not at all uncommon for later owners to bind works together (binding was expensive, and separate from publishing).
Our griffins are in this collection, TWICE. One version is another imprint the same rather squished version we saw issued by Beatus in 1601, the other is one we haven’t seen before. It’s roughly similar to the one above it, but there are some very subtle differences in detail, especially along the left and right edge. And of course, it’s paired with yet another secondary border. Original inclusion, or the result of later co-binding? Your guess is as good as mine. The book is here, it’s in the Clark Art Institute Library’s collection.


1660
Skip forward even further, now 63 years since the griffins appeared. Rosina Helena Furst/Paul Furst’s Model Buch Teil.1-2 printed in Nurnberg in 1660 offered a collection of older designs in addition to new ones. There were four in his series. This particular binding combines books 1 and 2. Lotz cites volumes one and 2 as 59 and 60, each with multiple surviving copies. For what it’s worth the Furst books are the first one that mention knitting as a possible mode of use for graphed patterns, and very possibly the first that is credited either in whole or in part to a female author. Some sources credit Paul Furst as the publisher and Rosina Helena Furst as the author, others attribute the entire work to Paul, or imply that Rosina Helena took over the family business after Paul’s death. In any case, they were prolific publishers, and continued to revise, and re-release modelbooks for at least a good 20 years. They did recast the legacy images to meet changing tastes, but it’s clear that our griffin has deeply informed this later, slightly more graceful beast. Note that his pattern height number is different from the earlier ones because his spacing and borders are a different size. You can see this copy here.

1666
We continue on with the Furst Das Neue Modelbuch editions. This one is also from Nurnberg, and is a multi-volume set in the care of the Clark Art Institute Library. The parts are listed as Lotz 59b, 60a, 61b, and 62a. Again someone has inked in bits to indicate shading. But it’s clearly the same plate as the 1660 printing.

1728
This is about as late as I research. Here we are 131 years after first publication, and there is still interest in the griffins. At least in the Furst interpretation of them. This is from the workshop of J.C. Seigels Wittib, in Nurnberg, and is a reissue of the Fursts’ Model Buch Teil 1-2. Again from the Clark Art Institute Library. It also looks to have been hand-inked on top of the same plate print. But if one looks very closely, there are small mistakes in ink application with very slight differences between the two. Including a forgotten square that shows the + behind the ink in one and not the other. A clear indication that the solid black areas were additions, and not done during the print process. It also makes me think that the 1728 inker had a copy of the 1666 book and copied the annotations to the best of their ability. Does that mean that some books were sold pre-inked? Not impossible. You can make your own judgement here.

Stitched representations
I am still looking for these. Representations of other Siebmacher designs exist in monochrome and polychrome counted stitching, as well as in white openwork. His reclining stag is the most often seen through time, but his unicorns, peacocks, eagles, religious symbols, long neck swans, flower pots, and rampant lions grace some spot samplers of the 1600s and into the early 1700s – mostly but not exclusively German or Dutch in origin. I’ve seen the parrots, undines, and mermen in white darned pieces (lacis in addition to withdrawn thread darned work). And that reclining stag crossed the ocean to appear on some early American samplers as well. But I haven’t seen a stitched version of these griffins. Yet.
Of course I haven’t seen everything, and back room pieces are being digitized every day. If you’ve spotted the griffins in the wild, please let me know.
Conclusions
This really is more of an observational survey than an academic hypothesis based essay.
Originally, seeing this (and other Siebmacher designs) repeat across multiple modelbooks, I assumed that they all were produced from the same plate. But on closer examination we see that probably isn’t true.
It is safe to say that there is a strong continuity of design here. And an interesting cross pollination among publishers. Was it tribute, licensing, sharing, or a bit of light plagiarism? We cannot tell from just examining the printings. But we can say that over the course of 131 years there were at least four and possibly five plates made based on the original griffin design, yet all are immediately identifiable as springing from the same source. I’m sure there are scholars who have delved into the interrelationships in the early printing industry, and have described other migrations of text or illustration among printing houses. Perhaps this look at a single pattern book plate will help inform their future musings.
We can also say that these design plates were used by a variety of prolific printers in Germany in response to what must have been continuing demand for pattern books. I say that because they were obviously selling well enough to warrant production over a long span of time, in spite of their largely offering up the same content over and over with only minor supplements. Also, in spite of the sometimes destructive nature of pattern replication at the time these early pattern books survived largely (but not totally) intact. For something so esoteric, with little literary value, they were seen as interesting and useful enough to retain in many libraries – to the delight of those who have rediscovered them again and again across centuries.
I just might have to stitch up these griffins, and in doing so know I’m helping to keep them alive.




